- Clone
- HK1.4 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus C
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2c, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
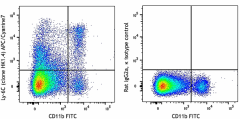
-
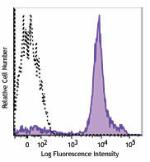
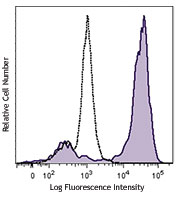
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD8a FITC and Ly-6C (clone HK1.4) APC/Cyanine7 (left) or Rat IgG2a, κ APC/Cyanine7 isotype control (right).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128025 | 25 µg | 104€ | ||||
| 128026 | 100 µg | 249€ | ||||
Most hematopoietic cells express one or more members of Ly-6 family. The expression of Ly-6 varies with development stage and activation. Ly-6C is a 14-17 kD GPI-linked surface protein expressed on mouse monocyte/macrophage cells, endothelial cells, neutrophils, and some T cell subsets. Ly-6C is reported to be an indicator of memory CD8+ T cells.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- L3 cloned CTL cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with APC/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is =0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Clone HK1.4 does not block the binding of clone RB6-8C58.
Additional reported applications (for relevant formats of this clone) include: in vitro activation of T cells1-3 and immunohistochemistry of frozen sections4. - Application References
-
- Jutila MA, et al. 1988. Eur. J. Immunol. 18:1819. (Activ)
- Herold KC, et al. 1990. Diabetes 39:815. (Activ)
- Havran WL, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 140:1034 (Activ)
- Flanagan K, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:3874. (IHC)
- Makaroff LE, et al. 2009. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106:4799. (FC)
- Zuber J, et al. 2009. Genes Dev. 23:877. (FC) PubMed
- Ribechini E, et al. 2009. Eur. J. Immunol. 39:3538.
- Ma C, et al. 2012. J. Leukoc. Biol. 92:1199.
- Watson NB, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:2796. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_10643867 (BioLegend Cat. No. 128025)
AB_10643867 (BioLegend Cat. No. 128026)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 14-17 kD protein (134 amino acids), member of the Ly-6 family of GPI linked protein. Ly6 family members share structure homology throughout a distinctive cystein rich protein domain that incorporates O-linked carbohydrates.
- Distribution
-
Ly-6C is expressed primarily on bone marrow myeloid populations, monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils, endothelial cells, and some T cell subsets. Ly-6C is also a marker of memory CD8+ T cells.
- Cell Type
- Endothelial cells, Macrophages, Monocytes, Neutrophils, T cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Jutila MA, et al. 1988. Eur. J. Immunol. 18:1819.
2. Cerwenka A, et al. 1998. J. Immunol. 161:97. - Gene ID
- 17067 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Ly-6C on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Ly-6C Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
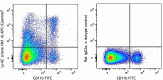
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 Pacific B... -
APC anti-mouse Ly-6C
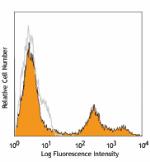
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 APC -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6C
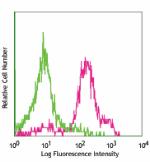
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with purified HK1.4,... 
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified Ly6C cl... -
Biotin anti-mouse Ly-6C
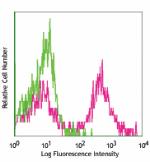
BALB/c bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 biotin, followed... -
FITC anti-mouse Ly-6C
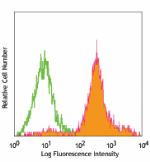
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 FITC (gated on ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ly-6C
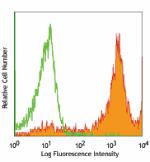
BALB/c bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 Alexa Fluor®... -
PE anti-mouse Ly-6C
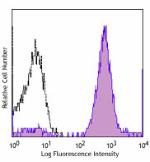
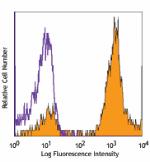
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clone HK1... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ly-6C
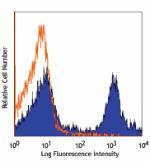
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 PerCP/Cyanine5.... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6C
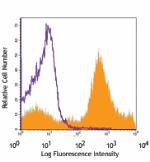
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 PE/Cyanine7 -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ly-6C
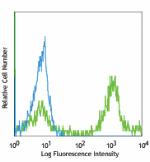
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with anti-mouse Ly-6C, HK1... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ly-6C
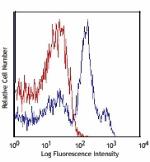
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with HK1.4 Alexa Fluor®... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6C
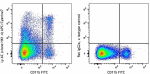
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD8a FITC ... -
PerCP anti-mouse Ly-6C
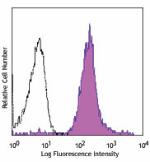
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clone HK1... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
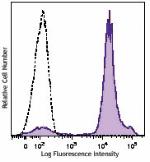
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clone HK1... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
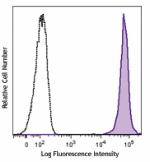
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
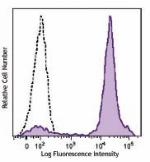
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
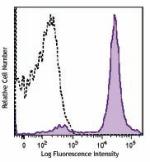
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
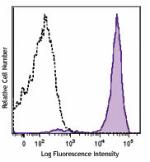
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6C (Maxpar® Ready)
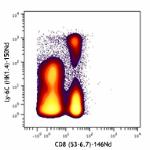
Mouse splenocytes stained with 150Nd-anti-Ly-6C (HK1.4) and ... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
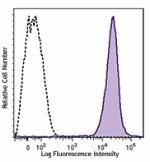
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ly-6C
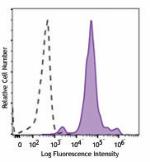
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
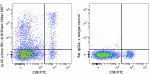
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ly-6C
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6C (clo... -
TotalSeq™-A0013 anti-mouse Ly-6C
-
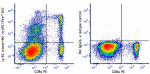
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse Ly-6C
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 FITC and Ly-... -
TotalSeq™-C0013 anti-mouse Ly-6C
-
TotalSeq™-B0013 anti-mouse Ly-6C
-
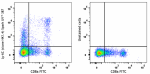
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse Ly-6C Antibody
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD8a ... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse Ly-6C

C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD8a FITC a... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse Ly-6C
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD8a ... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse Ly-6C
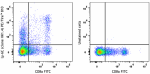
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD8a ... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse Ly-6C (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse Ly-6C (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse Ly-6C

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD8a ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us