- Clone
- 16A8 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- KIA, proliferation-related Ki-67 antigen
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
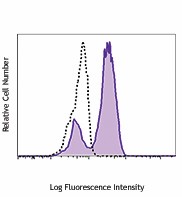
-

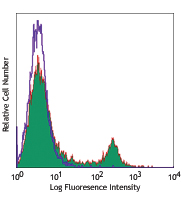
Con A-stimulated (three days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fixed and permeabilized with 70% ethanol, then stained with Ki-67 (clone 16A8) Pacific Blue™ (filled histogram) or rat IgG2a, κ Pacific Blue™ isotype control (open histogram).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 652421 | 25 µg | £101 | ||||
| 652422 | 100 µg | £262 | ||||
The nuclear protein Ki-67 was first identified by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67, which was generated by immunizing mice with nuclei of the L428 Hodgkin lymphoma cell line. Ki-67 protein plays an essential role in ribosomal RNA transcription and cell proliferation. Expression of Ki-67 occurs during G1, S, G2, and M phase, while in G0 phase the Ki-67 protein is not detectable. Ki-67 is strongly expressed in proliferating cells and has been reported as a prognostic marker in various tumors.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- E. coli expressed partial mouse Ki-67 recombinant protein, 1816-2163 aa.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Pacific Blue™ under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICFC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by our Ki-67 staining protocol below. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume or 100 µl of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Pacific Blue™ has a maximum emission of 455 nm when it is excited at 405 nm. Prior to using Pacific Blue™ conjugate for flow cytometric analysis, please verify your flow cytometer's capability of exciting and detecting the fluorochrome.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2564489 (BioLegend Cat. No. 652421)
AB_2564489 (BioLegend Cat. No. 652422)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 325 kD protein containing a forkhead-associated domain (FHA) and 13 tandem repeats
- Distribution
-
Nucleus and chromosome
- Function
- Required for cell cycle progression and proliferation
- Interaction
- Interacts with KIF15; binds to MKI67IP through FHA domain
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Cycle/DNA Replication, Transcription Factors
- Molecular Family
- Nuclear Markers
- Antigen References
-
1. Starborg M, et al. 1996. J. Cell. Sci. 109:143.
2. Byeon IJ, et al. 2005. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12:987.
3. Yerushalmi R, et al. 2010. Lancet. Oncol. 11:174.
4. Beltrami AP, et al. 2001. N. Engl. J. Med. 344:1750.
5. Sachsenberg N, et al. 1998. J. Exp. Med. 187:1295.
6. Nagy Z, et al. 1997. Acta. Neuropathol. 93:294. - Gene ID
- 17345 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Ki-67 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Ki-67 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | FC,WB,ICC,IHC-F |
| PE anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| APC anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| FITC anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
| Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse Ki-67 | 16A8 | ICFC |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-mouse Ki-67
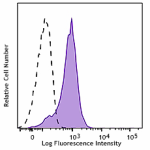
Con A-stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fix... 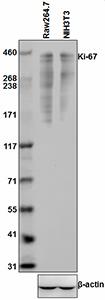
Total cell lysates (15 µg protein) from Raw264.7 and NIH3T3 ... 
TE‐71 cells were fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for te... 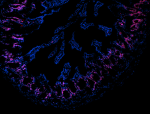
C57BL/6 mouse frozen intestine section was fixed with 4% par... -
PE anti-mouse Ki-67
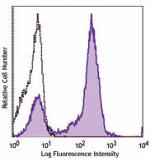
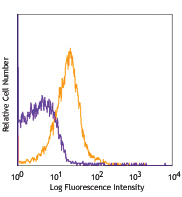
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated for 3 days with Co... -
APC anti-mouse Ki-67
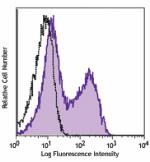
Con A+IL-2 stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ki-67
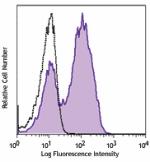
Con A-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c mouse splenocytes were fixe... -
FITC anti-mouse Ki-67
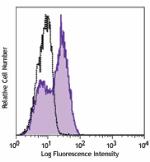
Con A-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c mouse splenocytes were fixe... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ki-67
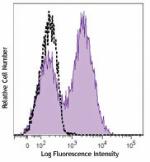
Con A+IL-2-stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ki-67
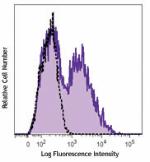
Con A+IL-2-stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ki-67
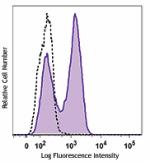
Con A-stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fix... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ki-67
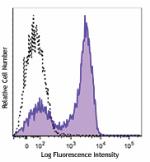
Con A+IL-2 stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ki-67
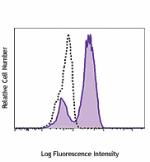
Con A-stimulated (three days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ki-67
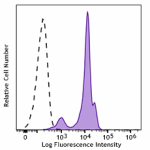
Con A+IL-2-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ki-67
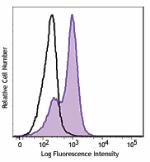
Con A+IL-2 stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ki-67
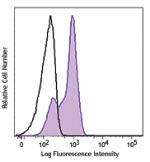
Con A + IL-2 stimulated (three days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ki-67
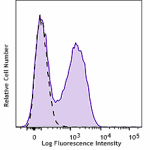
Con A-stimulated (2 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fix... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse Ki-67
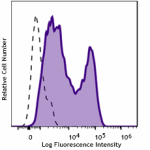
Con A+IL-2 stimulated (2 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes wer...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us