- Clone
- A20120B (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3)-Grabbing Nonintegrin (DC-SIGN), CLEC4L, DC-SIGN, DC-SIGN1, hDC-SIGN
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
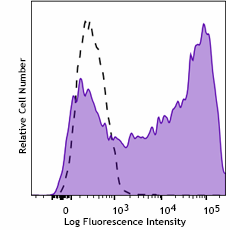
-

Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells were stained with purified anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN) (clone A20120B) (filled histogram) or purified rat IgG2b, κ isotype control (open histogram), followed by PE goat-anti-rat IgG.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 380402 | 100 µg | $258 | ||||
CD209, known as Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3)-Grabbing Nonintegrin (DC-SIGN), is a 44 kD type II transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the C-type lectin family. CD209 is expressed on myeloid dendritic cells, placental macrophages, liver and placental endothelial cells. CD209 binds to ICAM-3 (CD50), ICAM-2 (CD102), and Butyrophilin (BTN2A1), and mediates dendritic cell migration and T cell proliferation. Importantly, CD209 is a receptor of HIV-1 and some other viruses (such as West Nile virus, hepatitis C virus, etc), and some bacteria or parasites. It plays a critical role in capturing and internalizing those pathogens. LSP1 (leukocyte-specific protein 1) interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD209 and mediates transport of HIV to the proteasome.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Recombinant human CD209 protein, extracellular domain.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µL volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Clone A20120B can partially block the binding of clone 9E9A8 to target. It does not affect the binding of clone DCS-8C1, clone A20120F, and clone 14E3G7.
- RRID
-
AB_2924571 (BioLegend Cat. No. 380402)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- A 44 kD type II transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the C-type lectin family
- Distribution
-
Dendritic cells, Endothelial cells, Macrophages
- Function
- Functions in cell adhesion and pathogen recognition. This receptor recognizes a wide range of evolutionarily divergent pathogens with a large impact on public health, including leprosy and tuberculosis mycobacteria, the Ebola, hepatitis C, HIV-1 and Dengue viruses, and the SARS-CoV acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
- Cell Type
- Dendritic cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
- Fauci A. 1996. Nature. 384:529-34.
- Granelli-Piperno A, et al. 2005. J Immunol. 175:4265-73.
- Lai WK, et al. 2006. Am J Pathol. 169:200-8.
- Gene ID
- 30835 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD209 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD209 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN) | A20120B | FC |
| APC anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN) | A20120B | FC |
| PE anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN) | A20120B | FC |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN)
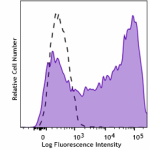
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells were stained with pur... -
APC anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN)
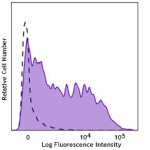
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells were stained with ant... -
PE anti-human CD209 (DC-SIGN)
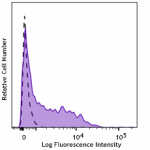
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells were stained with ant...
 Login/Register
Login/Register 








Follow Us