- Clone
- GoH3 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Workshop
- HCDM listed
- Other Names
- VLA-6 α chain, α6 integrin, integrin α6, ITGA6
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
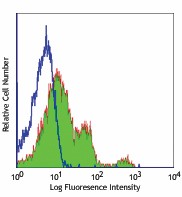
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified GoH3, followed by anti-rat IgGs FITC -
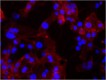
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were stained with anti-CD49f (clone GoH3) followed by DyLight™ 649 Goat anti-rat Ig secondary antibody (red), plus DAPI staining for nuclei (blue). Images were taken under 20x bin4 (Filter set: EX647/10x, Dichroic 665LP, EM 700/70x) at exposure 4s. Data provided by Er Liu and John Nolan, La Jolla Institute for Bioengineering.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 313602 | 100 µg | $119 | ||||
CD49f is a 120 kD integrin family member also known as VLA-6 α chain and α6 integrin subunit. CD49f associates with either integrin β1 (CD29) or integrin β4 (CD104) to form receptors (VLA-6 or α6β4 complex) for laminin and kalinin. CD49f is expressed on platelets, monocytes, T cells, placental trophoblasts, and epithelial and endothelial cells. CD49f is involved in adhesion and can act as a co-stimulatory molecule for T cell activation and proliferation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus, Rhesus
- Reported Reactivity
- African Green, Baboon, Capuchin Monkey, Cat, Cow, Chimpanzee, Cynomolgus, Dog, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep, Pig
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Mouse mammary tumor cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
ICC, IHC-F, IP, Block - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 2.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1,5, in vitro and in vivo blocking of cell binding to laminin and blocking the function of integrin a61,4, and immunohistochemistry of acetone-fixed frozen sections2,3,5. The GoH3 antibody has been reported to block laminin binding in vitro and to block integrin a6 function in vivo.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Georas SN, et al. 1993. Blood 82:2872. (IP, Block)
- Honda T, et al. 1995. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80:2899. (IHC)
- Sonnenberg A, et al. 1986. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34:1037. (IHC)
- Nakamura K, et al. 1997 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235:524. (Block)
- Sonnenberg A, et al. 1987 J. Biol. Chem. 262:10376. (IP, IHC)
- Deregibus MC, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-078709.
- Horwitz KB, et al. 2008. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:5774. PubMed
- Nardella C, et al. 2009. Sci Signal. 2:55. PubMed
- Xu T, et al. 2010. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:438. PubMed
- Stepp MA, et al. 2007. J Cell Sci. 120:2851. PubMed
- Jo M, et al. 2010. Cancer Res. 70:8948. PubMed
- Yoshino N, et al. 2000. Exp. Anim. (Tokyo) 49:97. (FC)
- Grange C, et al. 2011. Cancer Res. 71:5346. PubMed
- Lai KP, et al. 2012. Mol Endocrinol. 26:52. PubMed
- Oeztuerk-Winder F, et al. 2012. EMBO J. 31:3431. (FC) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_345296 (BioLegend Cat. No. 313602)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Integrin family, associates with β1 or β4, 120 kD
- Distribution
-
Platelets, monocytes, T cells, placental trophoblasts, epithelial and endothelial cells
- Function
- Adhesion, receptor for laminin and kalinin; laminin binding to VLA-6 induces T cell co-stimulation for proliferation and activation
- Ligand/Receptor
- With integrin β1 (CD29) forms VLA-6, with integrin β4 (CD104) forms a6β4 integrin; laminin and kalinin are ligands for these receptors
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Endothelial cells, Epithelial cells, Monocytes, Platelets, T cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Sonnenberg A, et al. 1990. J. Cell Biol. 110:2145.
2. Sonnenberg A, et al. 1990. J. Cell. Sci. 96:207.
3. Aumailley M, et al. 1990. Exp. Cell Res. 188:55.
4. Niessen CM, et al. 1994. Exp. Cell Res. 211:360. - Gene ID
- 16403 View all products for this Gene ID 3655 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD49f on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD49f Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased



Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human/mouse CD49f
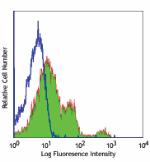
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified GoH... 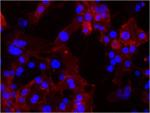
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were stained with anti-CD49f ... -
Biotin anti-human/mouse CD49f
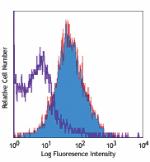
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated GoH3, fo... -
FITC anti-human/mouse CD49f
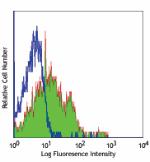
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with GoH3 FITC -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human/mouse CD49f
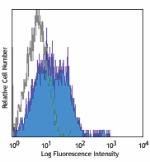
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human/mouse CD49f
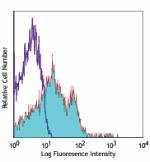
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with GoH3 Alexa F... -
PE anti-human/mouse CD49f
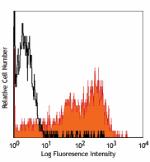
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with GoH3 PE -
APC anti-human/mouse CD49f
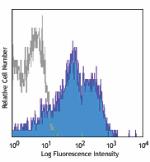
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human/mouse CD49f
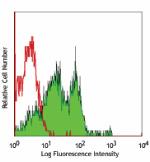
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with GoH3 PerCP/C... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human/mouse CD49f
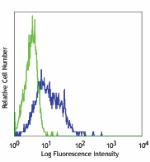
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with GoH3 Pacific... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human/mouse CD49f
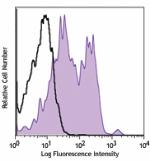
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human/mouse CD49f
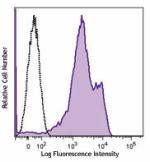
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... 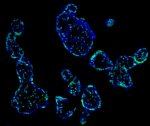
Human paraffin-embedded placenta tissue slices were prepared... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human/mouse CD49f
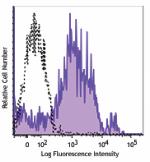
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human/mouse CD49f
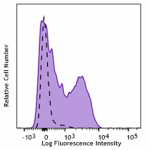
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD49f (... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human/mouse CD49f
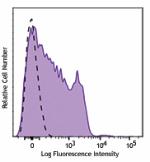
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
TotalSeq™-A0070 anti-human/mouse CD49f
-
TotalSeq™-C0070 anti-human/mouse CD49f
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human/mouse CD49f

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified GoH... 
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were stained with anti-CD49f ... -
TotalSeq™-B0070 anti-human/mouse CD49f
-
TotalSeq™-D0070 anti-human/mouse CD49f
-
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human/mouse CD49f

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... 
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-human/mouse CD49f (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-human/mouse CD49f (Flexi-Fluor™) Antibody
-
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human/mouse CD49f (Flexi-Fluor™)
 Login/Register
Login/Register 








Follow Us