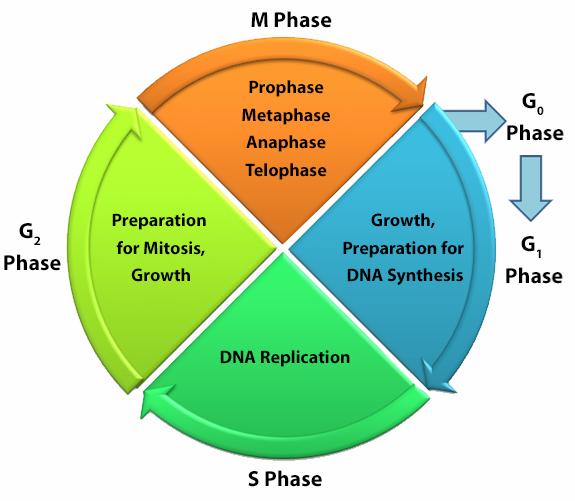
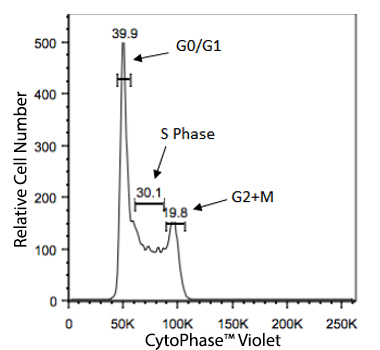
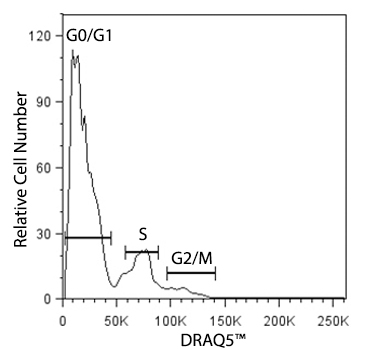
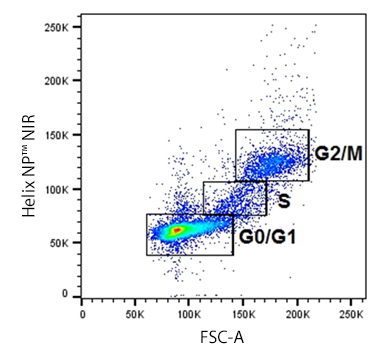
While some assays utilize antibodies to study cell health, proliferation, cell cycle or apoptosis, other types of experiments can rely on non-antibody based methods of assessment, often called non-antibody chemical probes. These are reagents that localize to an organelle or indicate health based on chemical characteristics like hydrophobicity, charge, size, and enzymatic activation.
Product Highlights
For our full listing of reagents, click through our sections below.

 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us