- Clone
- G8.8 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CD326, EGP40, MIC18, TROP1, KSA
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
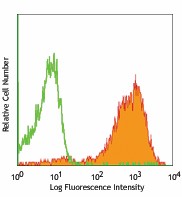
-

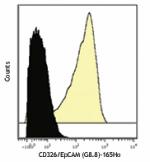
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) stained with G8.8 APC
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 118213 | 25 µg | ¥18,160 | |
| 118214 | 100 µg | ¥52,690 |
EpCAM (CD326) mediates calcium-independent homophilic cell to cell adhesion. It may also function as a growth factor receptor. It is thought to be involved in maintaining cells in position during proliferation. Expression of EpCAM seems to correlate inversely with the level of E-cadherin (CD324). EpCAM is considered important in tumor biology.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- TE-71 thymic epithelial cell line
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per 106 cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications for clone G8.8 (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemistry of frozen sections: acetone fixed1, with or without OCT embedding2,4, and spatial biology (IBEX)13,14.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Farr A, et al. 1991. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39:645. (FC, IHC)
- Dooley J, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:4331. (FC, IHC)
- Hinterberger M, et. al. 2010. Nat. Immunol. 11:512. (FC) PubMed
- Gracz AD, et al. 2010. Am J. Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:590. (IHC) PubMed
- Nudel I, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 186:891. PubMed
- Morimoto H, et al. 2012. Biol Reprod. 86:148. PubMed
- Ishii K, et al. 2012. Development. 139:1734. PubMed
- Takehashi M, et al. 2012. Biol Reprod. 86:178. PubMed
- Murakami R, et al. 2013. PLoS One. 8:73270. PubMed
- Taguchi K, et al. 2014. Mol Cell Biol. 34:900. PubMed
- Hirokawa Y, et al. 2014. Am J Physiol Gastrointerest Liver Physiol. 306:547. PubMed
- Ding X, et al. 2015. Cancer Res. 75:330. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_1134105 (BioLegend Cat. No. 118213)
AB_1134102 (BioLegend Cat. No. 118214)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 40 kD single-pass type 1 glycoprotein. 293 amino acids, with a 21 aa signal peptide, a 246 aa extracellular domain, a 21 aa transmembrane domain, and a 26 aa cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain contains two epidermal growth factor-like repeats.
- Distribution
-
Expressed on majority of epithelial cell membranes with the exception of adult squamous cells of the skin and a few specific epithelial cell types.
- Function
- Mediates calcium-independent homophilic cell-cell adhesion.
- Interaction
- CD326 displays hemophilic binding.
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD305 (LAIR-1), CD306 (LAIR-2), and Ep-CAM.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Epithelial cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Borkowski TA, et al. 1996. Eur. J. Immunol. 26:110.
2. Bergsagel PL, et al. 1992. J. Immunol. 148:590. - Gene ID
- 17075 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD326 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD326 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
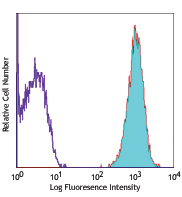
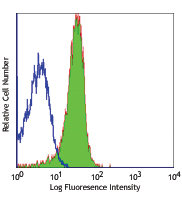
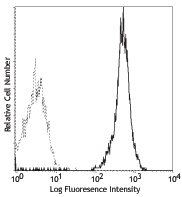
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
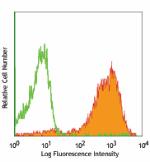
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) stained wi... -
Purified anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
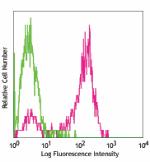
TE-71 cell line stained with G8.8 purified, followed by anti... -
Biotin anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
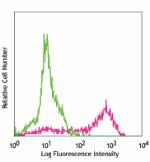
Mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line TE-71 stained with... -
PE anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
_Antibody_1_FC_100416.jpg&Width=150&altFmImage_path=&Crop=5)
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) cells were... -
FITC anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
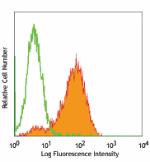
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) stained wi... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
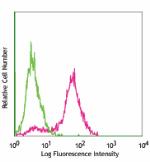
TE-71, mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line, stained wi... 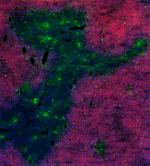
C57BL/6 mouse frozen thymus section was fixed with 4% parafo... 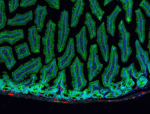
Dissected C57/B6 mouse stomach was immersed in 4% paraforma... 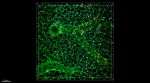
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse lung section... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
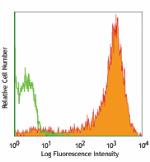
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) stained wi... 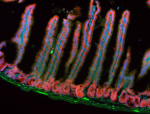
Dissected C57/B6 mouse small intestine was immersed in 4% p... 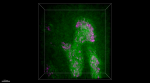
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse thymus tissu... 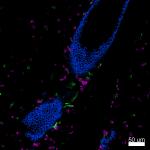
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse lung sample acquired using t... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
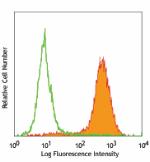
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) stained wi... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
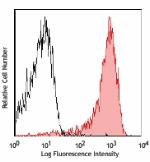
Mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line TE-71 stained with... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
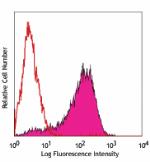
Mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line (TE-71) stained wi... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
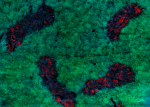
C57BL/6 mouse frozen thymus section was fixed with 4% parafo... 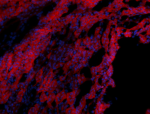
C57BL/6 mouse frozen kidney section was fixed with 4% parafo... 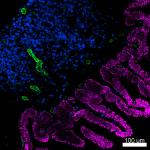
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse small intestine sample acqui... 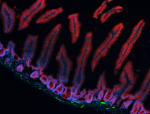
Dissected C57/B6 mouse small intestine was immersed in 4% p... Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse large intestine secti... 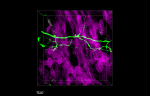
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse kidney tissu... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
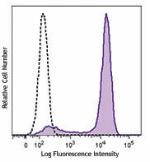
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) was staine... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
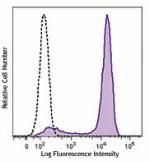
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) was staine... -
Purified anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM) (Maxpar® Ready)
Mouse TE-71 (top) or Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) (bottom) ce... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
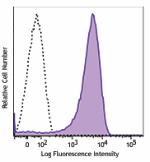
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) cells were... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
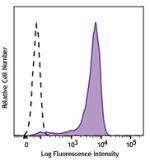
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) cells were... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
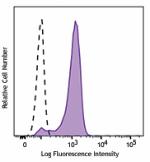
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) cells were... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
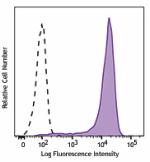
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) cells were... -
TotalSeq™-A0449 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
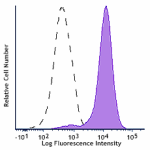
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) was staine... -
TotalSeq™-C0449 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
-
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
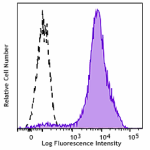
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) was staine... -
TotalSeq™-B0449 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
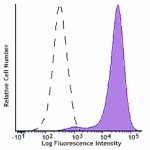
TE-71 (mouse thymic epithelial stromal cell line) was staine... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM)
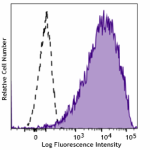
4T1 (a mouse triple negative breast cancer cell line) cells ... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse CD326 (Ep-CAM) (Flexi-Fluor™)














Follow Us