- Clone
- N418 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- αX integrin, integrin αX chain, CR4, p150, ITGAX
- Isotype
- Armenian Hamster IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
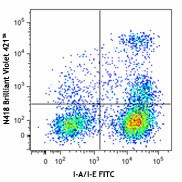
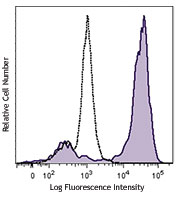
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E FITC and CD11c (clone N418) Brilliant Violet 421™ (top) or Armenian hamster IgG Brilliant Violet 421™ isotype control (bottom). -

-
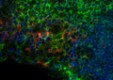
C57BL/6 mouse lymph nodes, fixed O/N in PLP, blocked with 10% rat serum, and stained with CD11c- BV421™(red), B220-Alexa Fluor® 647 (blue), and I-A/I-E-FITC (green) in 1% BSA and 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS. Images were acquired with an automated widefield microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti) and a CCD camera (QImaging Retiga 2000R). Emitted light was collected through 440/40, 525/50, and 700/75 nm bandpass filters. Images provided by Ann Haberman and Christine Podolski, Yale University.
CD11c is a 150 kD glycoprotein also known as αX integrin, CR4, and p150. CD11c forms a αXβ2 heterodimer with β2 integrin (CD18). It is primarily expressed on dendritic cells, NK cells, a subset of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL), and some activated T cells. The αXβ2 integrin plays an important role in cell-cell contact by binding its ligands: iC3b, fibrinogen, and CD54.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Armenian Hamster
- Immunogen
- Mouse spleen dendritic cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Brilliant Violet 421™ under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- µg sizes: 0.2 mg/mLµL sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IHC - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For immunofluorescent staining using the µg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. For immunofluorescent staining using µl sizes, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 421™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 421 nm. The standard bandpass filter 450/50 nm is recommended for detection. Brilliant Violet 421™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet™.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents. - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation3, immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections3, immunofluorescence microscopy5, 9 (Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugated N418 was used for IHC in frozen sections10), and spatial biology (IBEX)22,23.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Granucci F, et al. 1997. J. Immunol. 159:1794.
- Stokes RW, et al. 1998. J. Immunol. 160:5514.
- Metlay JP, et al. 1990. J. Exp. Med. 171:1753. (IHC, IP)
- Ma XT, et al. 2006. Cancer Research 66:1169.
- Chin RK, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 177:290. (IF)
- Cervantes-Barragan L, et al. 2007. Blood 109:1131. (FC) PubMed
- Turnquist HR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:7018. (FC) PubMed
- Benson MJ, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. doi:10.1084/jem.20070719. (FC) PubMed
- You Y, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 182:7343. (IF) PubMed
- Roland CL, et al. 2009. Mol. Cancer Res. 8:1761. (IHC, FC) PubMed
- Wikstrom M, et al.2006. J. Immunol. 177:913. PubMed
- Pericolini E, et al. 2008. J. Leukocyte Biol. 83:1286. PubMed
- Randall LM, et al. 2008. Infect. Immun.76:3312. PubMed
- Fahlen-Yrild L, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 183:5032. PubMed
- Osterholzer JJ, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 183:8044. PubMed
- Bankoti J, et al. 2010. Toxicol. Sci. 115:422. (FC) PubMed
- Eisenach PA, et al. 2010. J Cell Sci. 123:4182. PubMed
- Leppin K, et al. 2014. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55:3603. PubMed
- Sakai F, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:105370. PubMed
- Gibbins JD, et al. 2014. Blood. 124:2953. PubMed
- White CE, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:697. PubMed
- Lu X, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:2011. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_10897814 (BioLegend Cat. No. 117329)
AB_2563099 (BioLegend Cat. No. 117343)
AB_11219593 (BioLegend Cat. No. 117330)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Integrin α-chain, associates with integrin β2 (CD18), 150 kD
- Distribution
-
Dendritic cells, NK cells, intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL), some activated T cells
- Function
- Cellular adhesion
- Ligand/Receptor
- iC3b, fibrinogen
- Cell Type
- Dendritic cells, Epithelial cells, NK cells, T cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen Facts Book Academic Press.
2. Springer TA. 1994. Cell 76:301.
3. Lopez-Rodriguez C, et al. 1996. J. Immunol. 156:3780. - Gene ID
- 16411 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD11c on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What is the F/P ratio range of our BV421™ format antibody reagents?
-
It is lot-specific. On average it ranges between 2-4.
Other Formats
View All CD11c Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
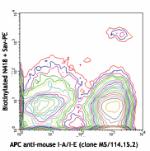
APC anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with N418 APC and PK136 PE -
Biotin anti-mouse CD11c
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... 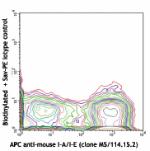
Frozen mouse spleen sections. Endogenous biotin blocking app... -
FITC anti-mouse CD11c
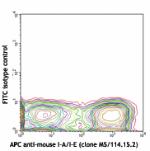
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... 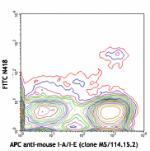
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... -
PE anti-mouse CD11c
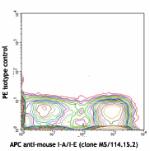
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... 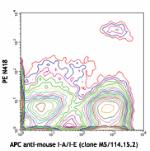
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... -
Purified anti-mouse CD11c
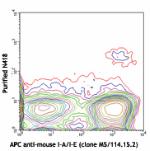
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... 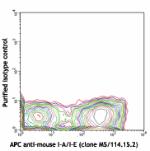
-
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD11c
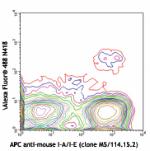
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... 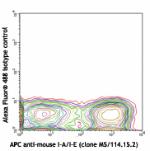
-
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD11c
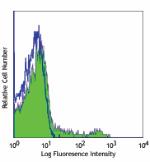
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with N418 Alexa Fluor® 647 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... 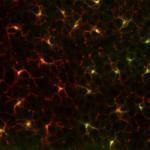
Fixed whole mount mouse epidermis Langerhans cells were stai... 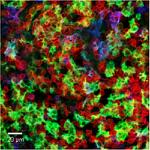
Live intravital mouse spleen imaging. PE CD11b (red) (clone ... 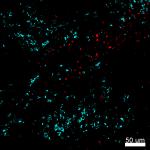
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse spleen sample acquired using... 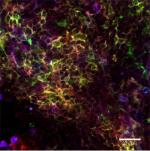
Fixed whole mount mouse spleen was stained with FITC CD172a ... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with APC anti-mouse I-A/I-... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E FITC and... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD11c
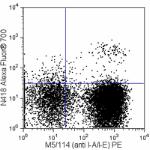
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with N418 Alexa Fluor®... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD11c
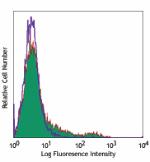
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Pacific Blue™ N... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD11c
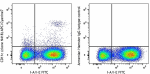
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E PE and C... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD11c
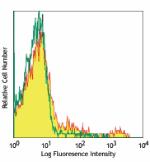
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with N418 PerCP/Cyanine5.5 -
PerCP anti-mouse CD11c
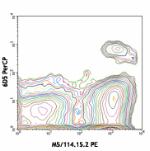
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with N418 PerCP and M5/114... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD11c
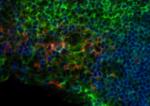
C57BL/6 mouse lymph nodes, fixed O/N in PLP, blocked with 10... 

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E FI... -
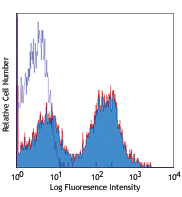
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse CD11c
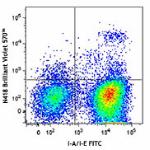
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E FI... 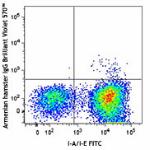
-
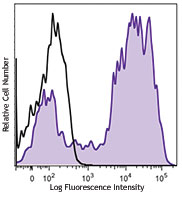
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E FITC and... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E AP... 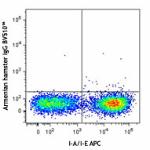
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E PE... 
-
Purified anti-mouse CD11c (Maxpar® Ready)

Mouse splenocytes stained with 147Sm-anti-CD45 (30-F11) and ... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD11c
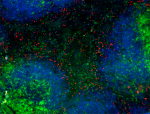
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 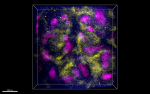
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E FITC and... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with mouse I-A/I-E Pe... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD11c
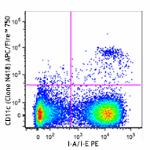
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E PE and CD11c (... 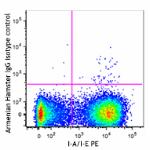
-
TotalSeq™-A0106 anti-mouse CD11c
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
TotalSeq™-B0106 anti-mouse CD11c
-
TotalSeq™-C0106 anti-mouse CD11c
-
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-mouse CD11c
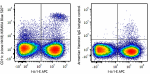
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with I-A/I-E APC and ... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse CD11c
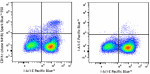
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with I-A/I-E (clone M5/114... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD11c
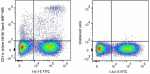
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse CD11c
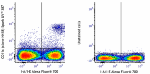
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD11c
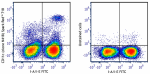
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
Spark Blue™ 515 anti-mouse CD11c
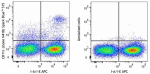
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were surface stained with anti-mou... -
PerCP/Fire™ 806 anti-mouse CD11c
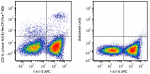
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I-E APC... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD11c (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark PLUS B550™ anti-mouse CD11c

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD11c Antibody

C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I-E (cl... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse CD11c Antibody

C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse I-A/I-E (cl...















Follow Us