- Clone
- DX5 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- α2 integrin, VLA-2 α chain, DX5, Integrin α2 chain, ITGA2
- Isotype
- Rat IgM, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
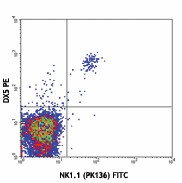
-

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 (PK136) FITC and DX5 PE
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108907 | 50 µg | $122 | ||||
| 108908 | 200 µg | $304 | ||||
DX5 antigen has been recently characterized as CD49b. It is a 150 kD integrin α chain also known as α2 integrin, VLA-2 α chain, and integrin α2 chain. CD49b non-covalently associates with CD29 (β1 integrin) to form the CD49b/CD29 complex known as VLA-2, a receptor for collagen and laminin. CD49b is expressed on platelets, the majority of NK cells, NKT cells, and a small subset of CD8+ T cells (this population can be significantly increased following viral infection). DX5 is used for the identification and isolation of NK cells, and is especially useful for identifying NK cells in mice lacking the NK1.1 antigen.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- IL-2-propagated NK1.1+ cells from C57BL/6 mice
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per 106 cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The DX5 clone detects cells expressing relatively high levels of CD49b and may not be useful for the detection of cells expressing low levels of CD49b. DX5 does not block NK cell killing or binding to collagen in vitro. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: complement-mediated cytotoxicity2 and immunohistochemical staining5 of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue sections as well as immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections10. The binding of DX5 antibody to splenic NK cells can be blocked by HMa2 antibody.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Arase H, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 167:1141. (FC)
- Sepulveda H, et al. 1999. J. Immunol. 163:1133.
- Norian LA and Allen PM. 2004. J. Immunol. 173:835. (FC)
- Andoniou CE, et al. 2005. Nature Immunology 6:1011.
- Oertelt S, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 177:1655. (IHC) PubMed
- Bourdeau A, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2006-08-044370.
- Charles N, et al. 2010. Nat. Med. 16:701. (FC) PubMed
- Qui Q, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:1681. (FC) PubMed
- Busche A, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 186:2918. PubMed
- Kim HR, et al. 2011. Nephrology 16:545. (IHC) PubMed
- Seyoum B, et al. 2011. Vaccine. 29:8002. PubMed
- Younos IH, et al. 2012. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:245. PubMed
- Honjo K, et al. 2012. PNAS. PubMed.
- Huang HN, et al. 2013. Biomaterials. 34:10151. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_313414 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108907)
AB_313415 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108908)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Integrin α chain, 150 kD
- Distribution
-
NK cells, subset of T cells
- Function
- Adhesion
- Ligand/Receptor
- Collagen, laminin
- Cell Type
- NK cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Arase H, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 167:1141.
2. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
3. Sasaki K, et al. 2003. Int. Immunol. 15:701.
4. Inoue O, et al. 2003. J. Cell Biol. 160:769. - Gene ID
- 16398 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD49b on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All CD49b Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| APC anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| Biotin anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| FITC anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| PE anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| Purified anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC,IHC-P,IHC-F |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
| APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells) | DX5 | FC |
Customers Also Purchased


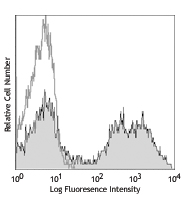
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
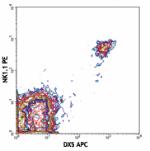
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 PE and DX5 APC -
Biotin anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
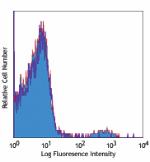
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated DX5, fol... -
FITC anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
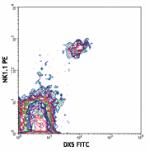
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 PE and DX5 FITC -
PE anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 (PK136) FITC an... -
Purified anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
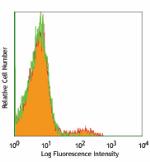
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with DX5 purified, followe... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
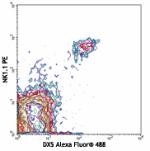
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 PE and DX5 Alex... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
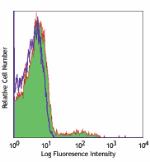
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with DX5 Alexa Fluor® ... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
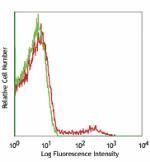
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with DX5 PerCP/Cyanine5.5 -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
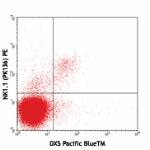
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with NK1.1 (PK136) PE and ... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
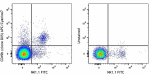
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with NK-1.1 FITC and ... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse NK-1.... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with NK1.1 Alexa Fluo... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD49b (pan-NK cells)
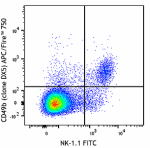
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse NK-1.1 FITC...
 Login/Register
Login/Register 














Follow Us