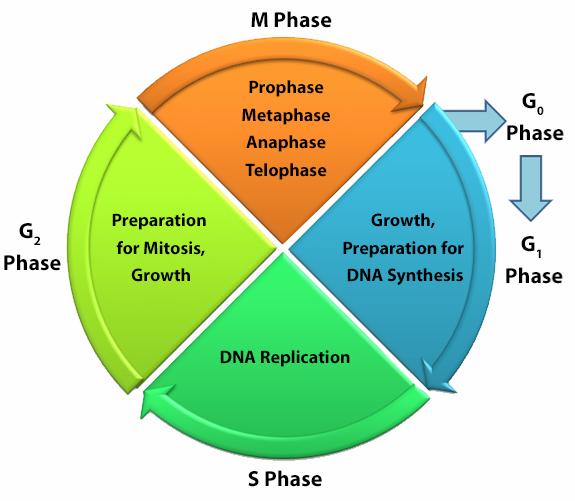
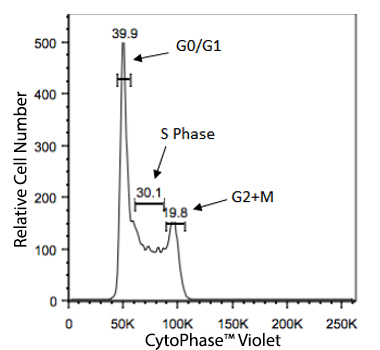
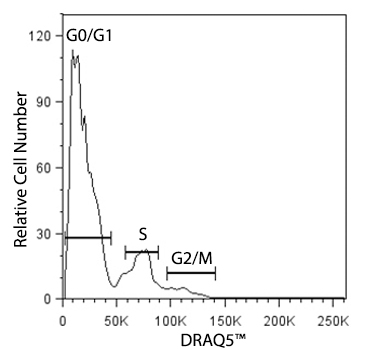
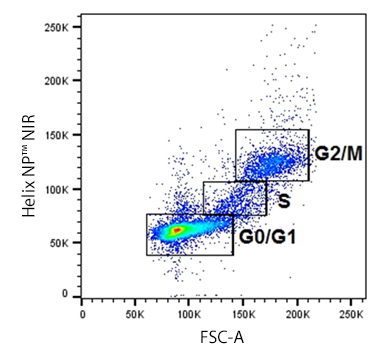
Cellular division for any cell type is dependent on the inherent function, location and the response of cells to repair, apoptosis, or death. To divide, cells must duplicate a copy of their DNA, increase mitochondrial density, and assemble/synthesize microtubules during interphase. G2 is a checkpoint stage of interphase where the cell has two sets of dsDNA and must commit to mitosis. Mitosis is the actual division stage where two daughter cells are created. There can be symmetrical or asymmetrical division depending on the cell and tissue type. Mitosis can be further subdivided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase as the nucleus undergoes division and chromatids are pulled away from one another. After mitosis, the cell will undergo the G0/G1 phase when the cells rest to become ready for the next round of replication.


 Login/Register
Login/Register 






Follow Us